Recreating the extracellular matrix (ECM)
X-Pure® medical grade gelatins: a leading choice of biomaterial for bioink
Bioprinted 3D models aim to recreate the extracellular matrix (ECM) to support successful cell growth and proliferation. X-Pure® gelatins, including X-Pure® GelMA and X-Pure® GelDAT modified gelatins, stand out as a premium choice of biomaterials to reproduce the dynamic mechanical properties of the ECM.
Living tissues can vary extensively in density and strength, therefore 3D printed models need to be able to accurately mimic these conditions. X-Pure (modified) gelatins offer tunable physicochemical properties. That enables the development of matrices which can have both high and low stiffness.
These can be use in tissue regeneration:
- bones,
- orthopaedic tissues,
- blood vessels,
- heart valves,
- musculoskeletal tissues,
- liver,
- nerves,
- and skin.1
Rousselot's dedication to excellence ensures that X-Pure® medical grade gelatins are designed to support the most cutting-edge bioink research and regenerative medicine advancements. The X-Pure range is purified, customizable and easily printable.
X-Pure in action
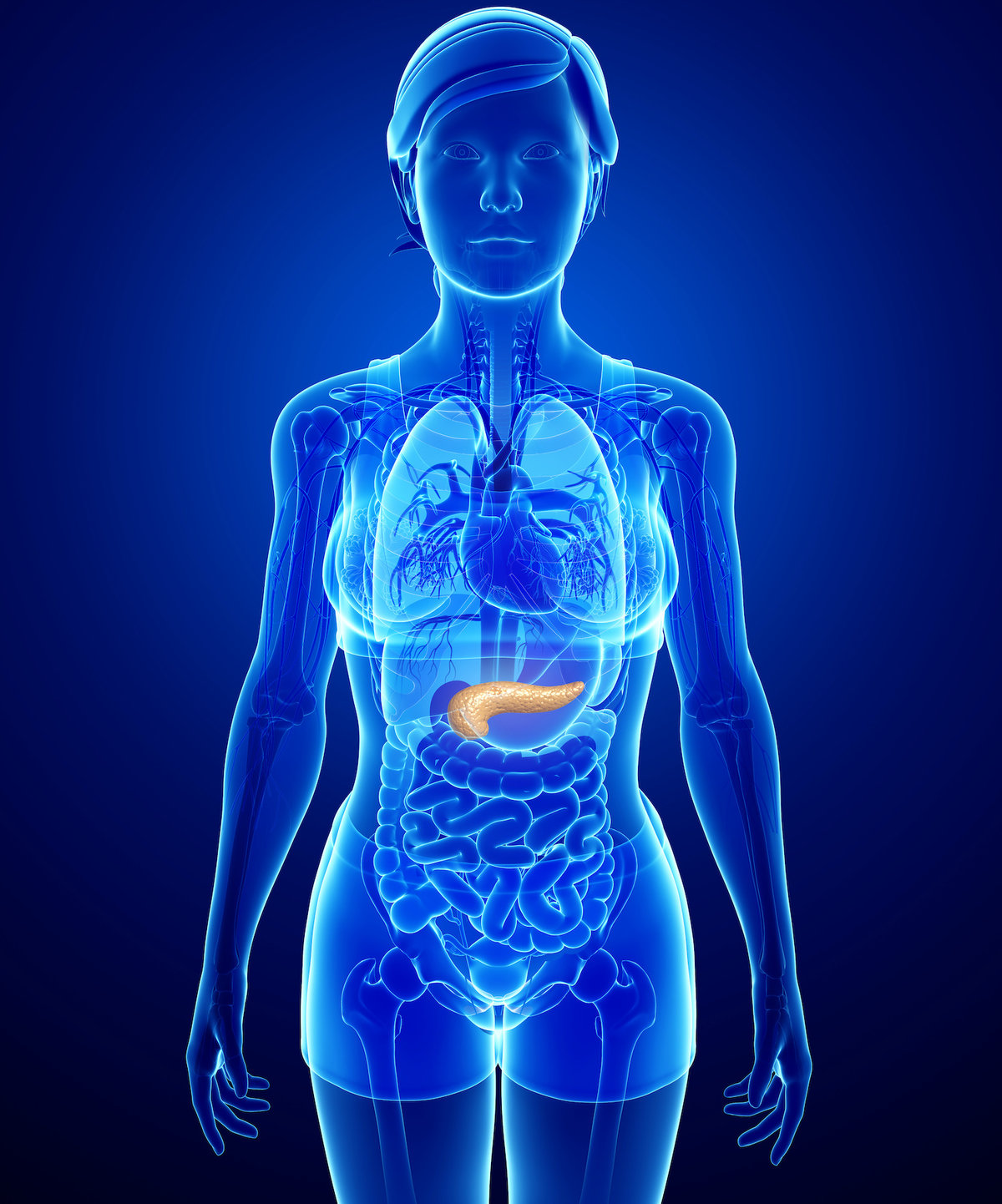
Find out about Rousselot’s role in the ENLIGHT project. Led by experts from academia and industry across Europe, the project aims to bioprint a 3D living model of pancreatic tissue. Rousselot been identified as a Key Innovator for this EU-funded innovation that uses X-Pure gelatin.
Why choose X-Pure?
1. Compliance – Overcome regulatory hurdles

All X-Pure® gelatins are compliant to the requirements of the major pharmacopoeia and support regulatory compliance with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745 and ISO 22442. The materials come with full traceability, readily available documentation and validated viral inactivation, helping to save time when reaching the clinic.
2. Tunable properties – Mimic each cell’s natural environment
X-Pure gelatins are fully customizable, allowing you to recreate the specific properties of the cell’s natural extracellular matrix and control the biodegradability process.
Different cells require different environments
X-Pure GelMA has tunable mechanical properties, including degree of modification, molecular weight, and can be used to create scaffolds of any shape and strength.
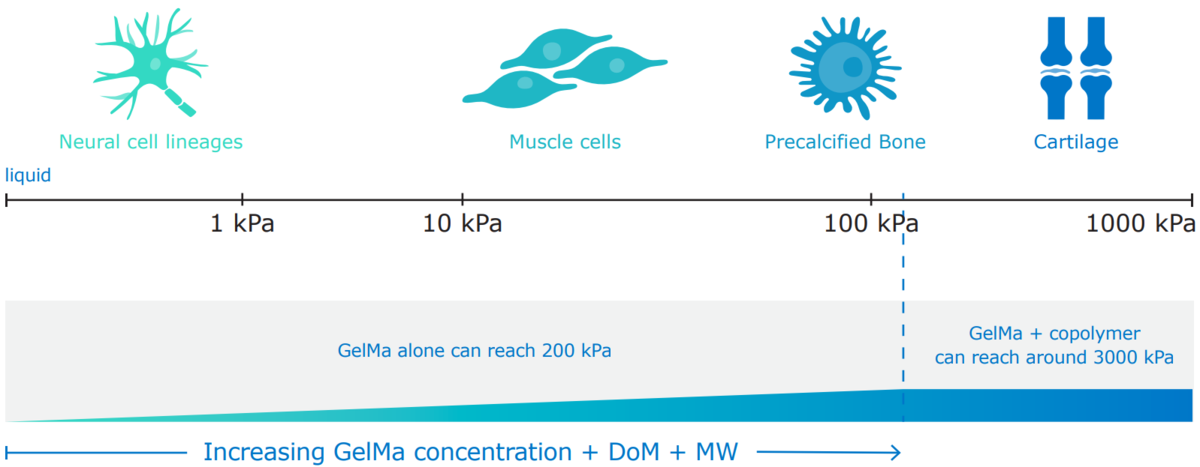
Examples of the tunability of GelMA’s physical characteristics.
The mechanical and degradation properties of GelMA hydrogels can be readily tuned by varying GelMA concentrations. Compressive and elastic moduli are tunable from a few kPa to a few hundred kPa, and degradation times can be varied from a few days to several months. This tunability makes GelMA hydrogels equally suitable as a bioink ingredient for cell culture or as a long-term wound healing solution.2
3. Consistency and scalability – Achieve predictable printing results

X-Pure® can help to avoid variability in your data, ensuring reproducible and repeatable results for efficient clinical translation and supporting the biocompatibility and biodegradability of the final application. X-Pure® gelatins and GelMAs are thermostable at 37°C, purified and consistently produced under GMP conditions.3
4. Stability – Bioprint with confidence

Producing hydrogels with predictable gel strength requires consideration of several important factors. Rousselot works on reliable protocols to obtain the desired gel strength and level of stability. Gelatin can be chemically crosslinked to produce hydrogel constructs that are stable at body temperature.
Read more
How to create the perfect GelMA formulation for specific applications: A story of temperature and photo-crosslinking.
5. High purity – Enhance safety and performance

Research has shown that using high-purity gelatin products can help boost cell proliferation. Endotoxin contamination in gelatin scaffolds can lead to tissue inflammation, biostructure rejection and even fatal shock. In addition, impurities in gelatin can lead to altered cellular responses and misinterpretation of results, causing delays in research translation.4
With ultra-low endotoxins (≤10EU/g), X-Pure® GelMA does not disrupt natural cell activity, supporting even the most sensitive in vivo applications.
Our experienced team will work closely with you to create a bio-ink for your specific 3D bioprinting application as well as supporting you through the regulatory process.
Read more
- Mimicking natural cell environments: how to select the optimal gelatin-based biomaterial for successful cell culture (blog)
- Discover the unique properties of gelatin in tissue engineering and 3D bioprinting (blog)
- Explore the expanding possibilities of gelatins and collagens in regenerative medicine (blog)
Upgrade your bioprinting with X-Pure GelMA
- Biocompatible
- Thermoreversible before crosslinking
- Thermostability at 37°C after crosslinking
- Biodegradable
- Purified (≤10EU/g)
- Excellent printability
References:
- Derakhshanfar, S., Mbeleck, R., Xu, K., Zhang, X., Zhong, W. and Xing, M., 2018. 3D bioprinting for biomedical devices and tissue engineering: A review of recent trends and advances. Bioactive materials, 3(2), pp.144-156
- Xin Zhao et al. 2015. Photocrosslinkable Gelatin Hydrogel for Epidermal Tissue Engineering Adv. Healthcare Mater. DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201500005
- IPEC. Excipient Good Manufacturing Practices Guide, 2022
- Heinrich, M.A., M. Mangia, and J. Prakash. 2021. Impact of endotoxins on bioengineered tissues and models. Trends Biotechnol.
![[Translate to Chinese:] 3D printing [Translate to Chinese:] 3D printing of gelatin](https://d1ip4j1950xau.cloudfront.net/_processed_/d/3/csm_3dprinting%20gelatin_0479951586.jpg)