How to choose the right biomaterial for safe and effective embolization?
Recent advances in embolization applications
As technology has advanced, surgical procedures have progressed from complex open surgery to minimally invasive interventions that have fewer complications, offering better outcomes for patients and lower costs for healthcare systems. Blood vessels are a common route of entry into the body and, through an endovascular approach, virtually any organ can be accessed.1 A common method for targeting a lesion using an endovascular approach is to decrease blood flow to that part of the body – a procedure known as embolization.
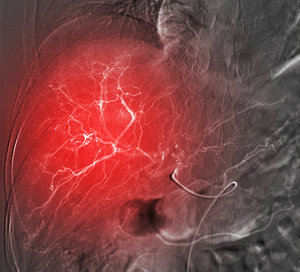
Embolization can be used to treat various conditions such as excessive internal bleeding, abnormal connections between blood vessels or other abnormal tissue growth. Today, embolization is also being used for an increasing range of biomedical applications, such as local pain management and osteoarthritis. For example, transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) techniques have recently been deployed to treat painful musculoskeletal conditions due to abnormally inflamed or hypervascular tissues. The idea is that by blocking the vascular supply, the pathologic tissue will no longer be a nociceptive trigger or produce pro-inflammatory mediators, and therefore pain will resolve. 2,3
Embolization is also being used in cancer treatment, where the goal is to prevent the flow of blood and oxygen to the tumour by blocking the blood vessels that serve it. Embolization can also be combined with other therapies such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), in which chemotherapeutic drugs are delivered in a more local manner to reduce side-effects and increase their efficacy, while also blocking blood flow to the tumour.
Can gelatin support embolization applications?
Depending on the condition, an embolizing agent provides a temporary or permanent closure. To ensure therapeutic effectiveness and safety the embolization agent has to be customized for the condition and requires specific properties.
Derived from the natural protein collagen, gelatin is biocompatible with the human body and therefore it is less likely to trigger immune responses or cause adverse reactions, promoting better patient outcomes.
Blood flow can be restored after the procedure
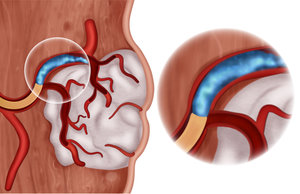
Gelatin is also biodegradable, breaking down naturally in the body over time, minimizing the risk of long-term complications associated with permanent implants. As the embolizing material degrades, the blood vessel reopens and blood flow is restored, while degradation products are safely resorbed by the body. The biodegradation rate of gelatin can be tailored, based on the specific needs of the procedure and can be tuned to match the desired persistence, from hours to weeks.
Gelatin based embolization agents can be used as a delivery system for chemotherapy drugs, radiotherapeutic agent and other compounds. For example, they can be easily mixed with iodinated contrast agents allowing interventional radiologists to visualise the embolic material’s precise location during the procedure.
What are the advantages of X-Pure?
X-Pure® is one of the purest gelatins available and it’s currently being used as a biomaterial for several embolization therapies. It not only supports safe and effective medical interventions but it can also be easily molded into different shapes and sizes, including microspheres, which are commonly used in embolization procedures. This flexibility in shaping and control over particle size allows for customization of the embolising agents, enabling physicians to target specific vessels or tissues more accurately.
Tailormade X-Pure gelatins for customized embolization
Rousselot’s X-Pure gelatins have been designed to address the specific requirements of embolization procedures. Offering regulatory compliance, customizability, purity, and batch-to-batch consistency, X-Pure can support a wide range of embolization applications, including TAE, TACE, and radioembolization. X-Pure gelatins are used in approved and marketed medical devices in the US and Asia.
Key features of X-Pure gelatin for embolization:
- Tailor-made gelatin: Customizable X-Pure gelatin can be designed to your specific application requirements for optimal performance and seamless product manufacturing.
- Consistency: With consistent quality and uniform product properties, X-Pure gelatins are designed to reduce procedural variability.
- Purity: X-pure gelatins with low endotoxins levels (<10 endotoxin units (EU)/g) help to ensure safe and effective medical devices.
- Documentation: All Rousselot products come with supporting documentation for compliance of medical devices with the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) ((EU) 2017/745), documented traceability up to the farm (ISO 22442-2), validated viral inactivation (ISO 22442-3) and IPEC GMP Compliance.
The future of embolization
X-Pure gelatin's biocompatibility and tunable properties make it a promising candidate for the future of embolization. As researchers continue to refine gelatin-based embolic agents and explore their potential applications, the pathway to safer and more effective embolization procedures becomes increasingly clear. However, progress in this field hinges not only on biomaterial innovation but also on collaboration among experts in biomaterial science, radiological imaging, and interventional radiology. Through coordinated efforts, the medical community can continue to enhance embolisation techniques, offering patients with various vascular conditions improved outcomes and better quality of life.
References:
Hu, J., Albadawi, H., Chong, B. W., Deipolyi, A. R., Sheth, R. A., Khademhosseini, A., & Oklu, R. (2019). Advances in Biomaterials and Technologies for Vascular Embolization. Advanced materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla.), 31(33), e1901071.
Kishore, S., Sheira, D., Malin, M. L., Trost, D. W., & Mandl, L. A. (2022). Transarterial Embolization for the Treatment of Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review of Indications, Safety, and Efficacy. ACR open rheumatology, 4(3), 209–217.
Gremen, E., Frandon, J., Lateur, G., Finas, M., Rodière, M., Horteur, C., Benassayag, M., Thony, F., Pailhe, R., & Ghelfi, J. (2022). Safety and Efficacy of Embolization with Microspheres in Chronic Refractory Inflammatory Shoulder Pain: A Pilot Monocentric Study on 15 Patients. Biomedicines, 10(4), 744.